はじめに
調べても分からなかったので自分なりにやってみる黒魔術シリーズです。もっといい方法があれば教えてください。
この記事では、ggplot2パッケージを利用してバイナリツリーのグラフを作成します。
【他の内容】
【目次】
ggplot2で二分木を作図したい
ggplot2パッケージを利用して、二分木(二進木・バイナリーツリー・binary tree)のグラフを作成する。
利用するパッケージを読み込む。
# 利用パッケージ library(tidyverse)
この記事では、基本的に パッケージ名::関数名() の記法を使っているので、パッケージを読み込む必要はない。ただし、作図コードについてはパッケージ名を省略しているので、ggplot2 を読み込む必要がある。
また、ネイティブパイプ演算子 |> を使っている。magrittrパッケージのパイプ演算子 %>% に置き換えても処理できるが、その場合は magrittr を読み込む必要がある。
二分木の作成
まずは簡易版として、「上から下」また「左から右」方向に欠損なくノード(要素)が並ぶ二分木のグラフを作成する。
ただし、最初のノード(要素)のインデックスを1とする(Rが1からなので)。インデックスを0から割り当てる場合は「ggplot2でn分木を作図したい - からっぽのしょこ」を参照のこと。
ノード数を指定して、値を作成する。
# ノード数を指定 N <- 31 # (簡易的に)値を作成 a <- 1:N head(a)
## [1] 1 2 3 4 5 6
ノード(頂点・節)の数を整数 N として、N 個の値を数値(などの)ベクトル a として作成する。a のみが与えられる場合は、a の要素数を N とする。
ノードの描画用のデータフレームを作成する。
# ラベル位置の調整値を指定 d <- 0.6 # ノードの座標を作成 node_df <- tibble::tibble( value = a, index = 1:N, depth = floor(log2(index)), col_idx = index - 2^depth + 1, # 深さごとのノード番号 coord_x = (col_idx * 2 - 1) * 1/(2^depth * 2), label_offset = dplyr::if_else( condition = index%%2 == 0, true = 0.5+d, false = 0.5-d ) # ラベル位置を左右にズラす ) node_df
## # A tibble: 31 × 6 ## value index depth col_idx coord_x label_offset ## <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> ## 1 1 1 0 1 0.5 -0.1 ## 2 2 2 1 1 0.25 1.1 ## 3 3 3 1 2 0.75 -0.1 ## 4 4 4 2 1 0.125 1.1 ## 5 5 5 2 2 0.375 -0.1 ## 6 6 6 2 3 0.625 1.1 ## 7 7 7 2 4 0.875 -0.1 ## 8 8 8 3 1 0.0625 1.1 ## 9 9 9 3 2 0.188 -0.1 ## 10 10 10 3 3 0.312 1.1 ## # ℹ 21 more rows
この例では、根ノードのインデックスを 、深さを
とする。
各ノード(要素) の値
とインデックス
をデータフレームに格納して、深さ
を計算する。各ノード(インデックス)の深さは
で求まる。
は、床関数(
floor())で、 以下の最大の整数(小数点以下の切り捨て)を表す。
各深さにおけるノード番号(位置)を 、左端のノードを
で表すことにする。左から1番目(左端)のノードのインデックスは
なので、左からの位置は
で求まる。
各分岐をシンメトリーに描画する場合は、深さごとに、ノード数の2倍の個数 に等間隔
に分割した
番目の位置にノードを配置する。このとき、x軸の範囲は0から1になる。
ラベル位置の調整用の値を作成する。この例では、インデックスが偶数の場合は左にズラすために0.5以上の値、奇数の場合は右にズラすために0.5以下の値を格納する。
エッジの描画用のデータフレームを作成する。
# エッジの座標を作成 edge_df <- dplyr::bind_rows( # 子ノードの座標 node_df |> dplyr::filter(depth > 0) |> # 根を除去 dplyr::mutate( edge_id = index, node_type = "childe" # (確認用) ), # 親ノードの座標 node_df |> dplyr::filter(depth > 0) |> # 根を除去 dplyr::mutate( edge_id = index, node_type = "parent", # (確認用) depth = depth - 1, index = index %/% 2, col_idx = index - 2^depth + 1, # 深さごとのノード番号 coord_x = (col_idx * 2 - 1) * 1/(2^depth * 2) ) ) |> dplyr::select(!label_offset) |> dplyr::arrange(edge_id, depth) edge_df
## # A tibble: 60 × 7 ## value index depth col_idx coord_x edge_id node_type ## <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <chr> ## 1 2 1 0 1 0.5 2 parent ## 2 2 2 1 1 0.25 2 childe ## 3 3 1 0 1 0.5 3 parent ## 4 3 3 1 2 0.75 3 childe ## 5 4 2 1 1 0.25 4 parent ## 6 4 4 2 1 0.125 4 childe ## 7 5 2 1 1 0.25 5 parent ## 8 5 5 2 2 0.375 5 childe ## 9 6 3 1 2 0.75 6 parent ## 10 6 6 2 3 0.625 6 childe ## # ℹ 50 more rows
親子ノードを結ぶエッジ(辺・枝)の描画用に、子ノードのインデックスを 、親ノードのインデックスを
として、子ノード
と親ノード
の座標データをそれぞれ作成して行方向に結合する。
子ノードのデータは、各ノードのデータ node_df から根ノードのデータ(行)を取り除く。
親ノードのデータは、各ノードのデータから根ノードのデータを取り除いて親ノードのデータを計算する。親ノードの深さは 、インデックスは
で求まる。座標などは
を用いて先ほどと同様にして計算する。
元のノードのインデックスをエッジIDとする。
バイナリツリーを作成する。
# ツリーの高さを取得 max_h <- max(node_df[["depth"]]) max_h <- floor(log2(N)) # 縦方向の余白の調整値を指定 d <- 0.1 # 二分木を作図 ggplot() + geom_path(data = edge_df, mapping = aes(x = coord_x, y = depth, group = edge_id), linewidth = 1) + # エッジ geom_point(data = node_df, mapping = aes(x = coord_x, y = depth), size = 12, shape = "circle filled", fill = "white", stroke = 1) + # ノード geom_text(data = node_df, mapping = aes(x = coord_x, y = depth, label = value), size = 5) + # 値ラベル geom_text(data = node_df, mapping = aes(x = coord_x, y = depth, label = index, hjust = label_offset), size = 4, vjust = -2, color = "blue") + # 位置ラベル scale_x_continuous(labels = NULL, name = "") + scale_y_reverse(breaks = 0:max_h, minor_breaks = FALSE) + coord_cartesian(xlim = c(0, 1), ylim = c(max_h+d, -d)) + labs(title = "binary tree", subtitle = paste0("height = ", max_h), y = "depth")
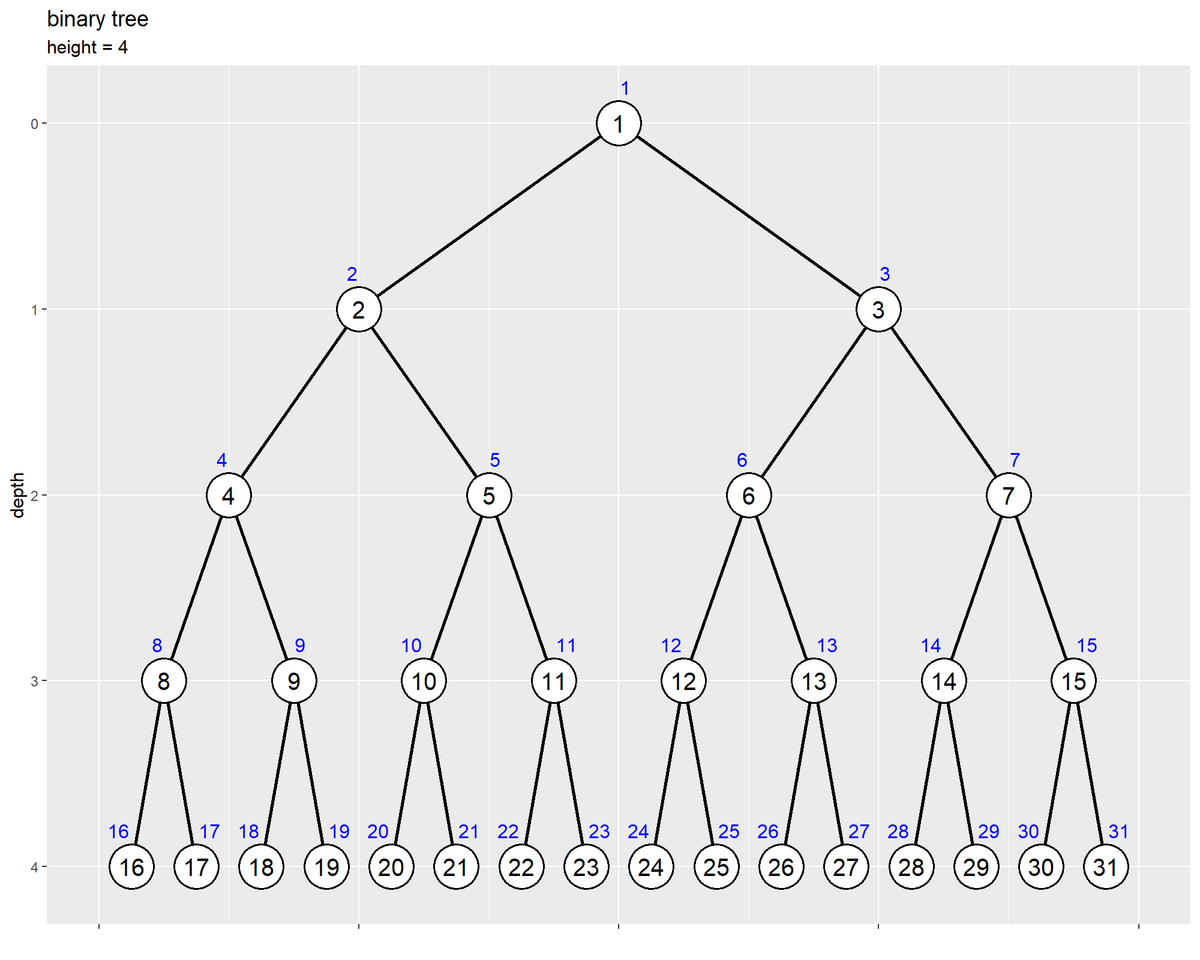
エッジとして geom_path() で線分を描画する。線分間が繋がらないように、group 引数にエッジIDを指定する。
ノードとして geom_point() で点を描画する。枠線と枠内を色分けする場合は、shape 引数に "*** filled" の形状を指定する。
ラベルを geom_text() でテキストを描画する。ノードやエッジと重ならないように表示する場合は、hjust, vjust 引数に値を指定する。この例では、インデックスが偶数なら左、奇数なら右にズラしている。
深さ(y軸の値)が大きくなるほど下になるように、scale_y_reverse() でy軸を反転する。
上の方法では、親子ノードの座標データを同じ列に持つデータフレームを作成して、geom_path() でエッジを描画した。次の方法では、親子ノードの座標データを別の列として持つデータフレームを作成して、geom_segment() でエッジを描画する。
エッジの描画用のデータフレームを作成する。
# エッジの座標を作成 edge_df <- dplyr::bind_cols( # 子ノードの座標 node_df |> dplyr::filter(depth > 0) |> # 根を除去 dplyr::select(!label_offset), # 親ノードの座標 node_df |> dplyr::filter(depth > 0) |> # 根を除去 dplyr::mutate( parent_depth = depth - 1, parent_index = index %/% 2, parent_col_idx = parent_index - 2^parent_depth + 1, # 深さごとのノード番号 parent_coord_x = (parent_col_idx * 2 - 1) * 1/(2^parent_depth * 2) ) |> dplyr::select(parent_index, parent_depth, parent_coord_x) ) edge_df
## # A tibble: 30 × 8 ## value index depth col_idx coord_x parent_index parent_depth parent_coord_x ## <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> ## 1 2 2 1 1 0.25 1 0 0.5 ## 2 3 3 1 2 0.75 1 0 0.5 ## 3 4 4 2 1 0.125 2 1 0.25 ## 4 5 5 2 2 0.375 2 1 0.25 ## 5 6 6 2 3 0.625 3 1 0.75 ## 6 7 7 2 4 0.875 3 1 0.75 ## 7 8 8 3 1 0.0625 4 2 0.125 ## 8 9 9 3 2 0.188 4 2 0.125 ## 9 10 10 3 3 0.312 5 2 0.375 ## 10 11 11 3 4 0.438 5 2 0.375 ## # ℹ 20 more rows
各ノードのデータと親ノードの座標データをそれぞれ作成して列方向に結合(別の列として追加)する。別の列にするために列名を変更して、先ほどと同様にして計算する。
バイナリツリーを作成する。
# ツリーの高さを取得 max_h <- max(node_df[["depth"]]) # 縦方向の余白の調整値を指定 d <- 0.1 # 二分木を作図 ggplot() + geom_segment(data = edge_df, mapping = aes(x = coord_x, y = depth, xend = parent_coord_x, yend = parent_depth), linewidth = 1) + # エッジ geom_point(data = node_df, mapping = aes(x = coord_x, y = depth), size = 12, shape = "circle filled", fill = "white", stroke = 1) + # ノード geom_text(data = node_df, mapping = aes(x = coord_x, y = depth, label = paste("a[", index, "]")), parse = TRUE, size = 5) + # 要素ラベル geom_text(data = node_df, mapping = aes(x = coord_x, y = depth, label = index, hjust = label_offset), size = 4, vjust = -2, color = "blue") + # 位置ラベル scale_x_continuous(labels = NULL, name = "") + scale_y_reverse(breaks = 0:max_h, minor_breaks = FALSE) + coord_cartesian(xlim = c(0, 1), ylim = c(max_h+d, -d)) + labs(title = "binary tree", subtitle = paste0("height = ", max_h), y = "depth")
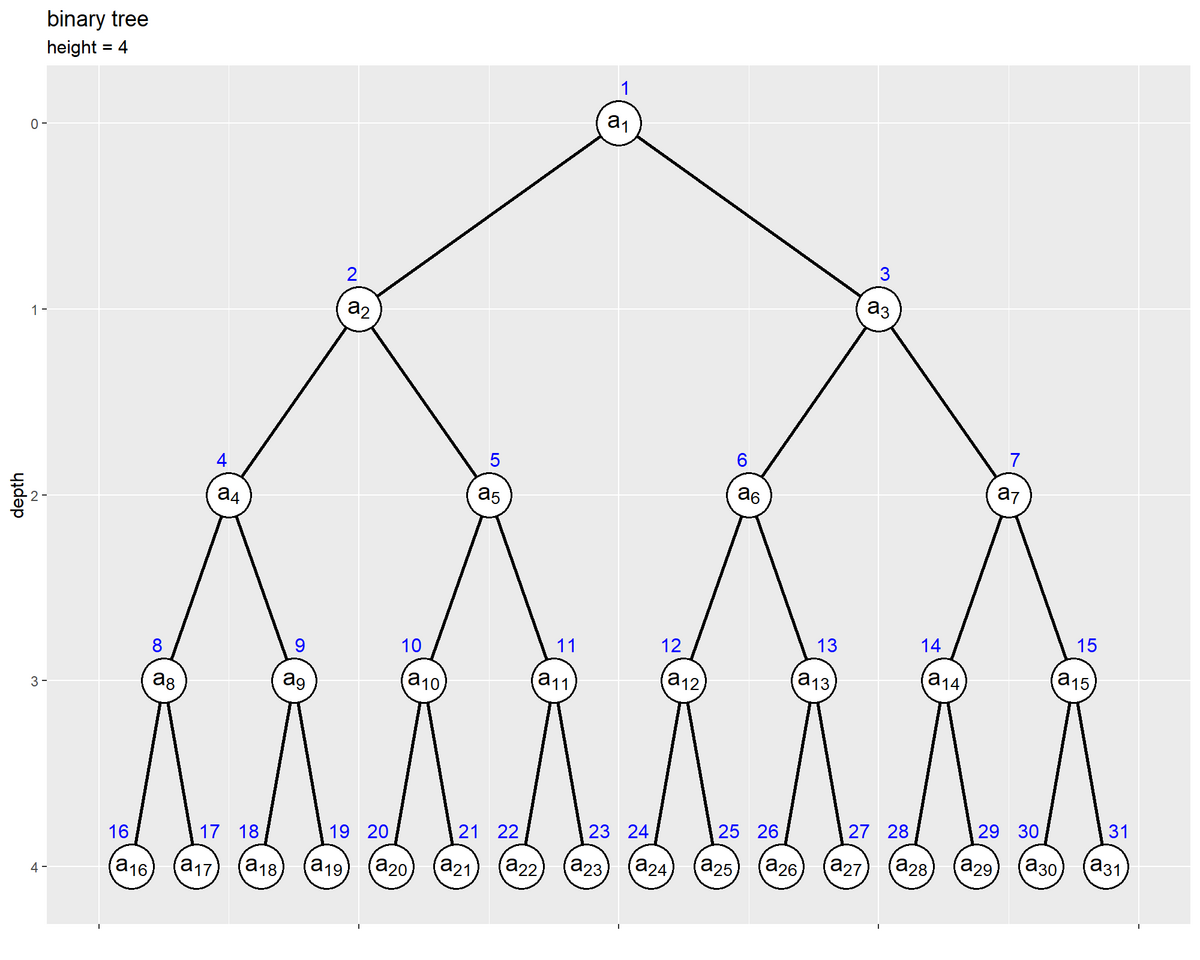
geom_segment() でエッジを描画する。始点の座標の引数 x, y に各ノードに関する値、終点の座標の引数 xend, yend に親ノードに関する値を指定する(始点と終点を入れ替えても作図できる)。
どちらの方法でもグラフ自体には影響しない。ただしこちらは(同じ図を作っても面白くないので)、ノードごとに値ラベルではなく要素ラベルを表示した。
部分木インデックスの計算
次は、二分木の剪定のために、部分木のインデックスを作成する処理を関数として実装する。
(手打ちで全てのインデックスを指定するのは嫌なので、)部分木の根ノードのインデックスを指定すると、部分木の全てのインデックスを返す関数を作成しておく。
# 部分木インデックスの定義 subtree <- function(root_index, max_index) { # 部分木の根インデックスを取得 parent_idx <- root_index[root_index <= N] |> sort() # インデックスの最大値を取得 N <- max_index # 親ごとに処理 childe_idx <- NULL for(i in parent_idx) { # 兄弟インデックスを作成 sibling_idx <- c(2*i, 2*i+1) # 子インデックスを格納 childe_idx <- c(childe_idx, sibling_idx[sibling_idx <= N]) # 最大位置を超えたら除去 } # 子がなければ再帰処理を終了 if(length(childe_idx) == 0) return(parent_idx) # 子孫インデックスを作成 descendant_idx <- subtree(childe_idx, N) # 部分木インデックスを格納 subtree_idx <- c(parent_idx, descendant_idx) |> sort() # 子孫インデックスを出力 return(subtree_idx) }
親ノードのインデックス を入力して、子ノードのインデックス
を格納していく処理を再帰的に行う。ただし、最大インデックス
を超える場合は含めない。
部分木の作成
二分木の部分木のグラフを作成する。
ノード数と部分木の根を指定して、部分木を作成する。
# ノード数を指定 N <- 63 # 部分木の根を指定 sub_root_idx <- c(3, 4, 22) # 部分木のインデックスを作成 sub_node_idx <- subtree(sub_root_idx, N) sub_node_idx
## [1] 3 4 6 7 8 9 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 22 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 ## [26] 34 35 36 37 38 39 44 45 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63
ノードの数(インデックスの最大値)を整数 N として指定する。
部分木の根ノードのインデックスを整数(複数の場合は整数ベクトル) sub_root_idx として指定して、subtree() で部分木のノードのインデックスを作成して sub_node_idx とする。
ノードの値から部分木に含まれないノードの値を削除する。
# 値を作成 a <- sample(x = 1:N, size = N, replace = TRUE) # 部分木以外のノードを剪定 a[!1:N %in% sub_node_idx] <- NA a
## [1] NA NA 34 35 NA 43 8 35 19 NA NA 2 10 12 36 29 21 49 4 NA NA 32 NA 19 18 ## [26] 4 55 52 1 37 52 53 37 17 27 1 11 41 44 NA NA NA NA 1 3 NA NA 24 4 63 ## [51] 24 1 52 4 63 23 4 47 60 32 60 50 8
N 個の値 a の内、sub_node_idx に含まれない要素を欠損値 NA に置き換える(代入する)。全てのインデックスと値を残すインデックスを %in% 演算子で比較して、! で TRUE, FALSE を反転することで置換できる。
ノードの描画用のデータフレームを作成する。
# ノードの座標を作成 d <- 0.5 node_df <- tibble::tibble( value = a, node_id = 1:N, index = dplyr::if_else( condition = !is.na(value), true = node_id, false = NA_real_ ), depth = floor(log2(index)), col_idx = index - 2^depth + 1, # 深さごとのノード番号 coord_x = (col_idx * 2 - 1) * 1/(2^depth * 2), label_offset = dplyr::if_else( condition = index%%2 == 0, true = 0.5+d, false = 0.5-d ) # ラベル位置を左右にズラす ) node_df
## # A tibble: 63 × 7 ## value node_id index depth col_idx coord_x label_offset ## <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> ## 1 NA 1 NA NA NA NA NA ## 2 NA 2 NA NA NA NA NA ## 3 34 3 3 1 2 0.75 0 ## 4 35 4 4 2 1 0.125 1 ## 5 NA 5 NA NA NA NA NA ## 6 43 6 6 2 3 0.625 1 ## 7 8 7 7 2 4 0.875 0 ## 8 35 8 8 3 1 0.0625 1 ## 9 19 9 9 3 2 0.188 0 ## 10 NA 10 NA NA NA NA NA ## # ℹ 53 more rows
「二分木の作成」のときと同様に処理する。ただし、ノードのID(通し番号)を node_id 列、値(要素)の欠損に応じて欠損させたIDを index 列とする。
値やインデックスが欠損値なので、座標データ(深さやx軸座標)の計算結果も欠損値になり、描画されない。
エッジの描画用のデータフレームを作成する。
# エッジの座標を作成 edge_df <- dplyr::bind_rows( # 子ノードの座標 node_df |> dplyr::filter(depth > 0, !index %in% sub_root_idx) |> # 根を除去 dplyr::mutate( edge_id = index, node_type = "childe" # (確認用) ), # 親ノードの座標 node_df |> dplyr::filter(depth > 0, !index %in% sub_root_idx) |> # 根を除去 dplyr::mutate( edge_id = index, node_type = "parent", # (確認用) depth = depth - 1, index = index %/% 2, col_idx = index - 2^depth + 1, # 深さごとのノード番号 coord_x = (col_idx * 2 - 1) * 1/(2^depth * 2) ) ) |> dplyr::select(!label_offset) |> dplyr::arrange(edge_id, depth) edge_df
## # A tibble: 92 × 8 ## value node_id index depth col_idx coord_x edge_id node_type ## <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> ## 1 43 6 3 1 2 0.75 6 parent ## 2 43 6 6 2 3 0.625 6 childe ## 3 8 7 3 1 2 0.75 7 parent ## 4 8 7 7 2 4 0.875 7 childe ## 5 35 8 4 2 1 0.125 8 parent ## 6 35 8 8 3 1 0.0625 8 childe ## 7 19 9 4 2 1 0.125 9 parent ## 8 19 9 9 3 2 0.188 9 childe ## 9 2 12 6 2 3 0.625 12 parent ## 10 2 12 12 3 5 0.562 12 childe ## # ℹ 82 more rows
「二分木の作成」のときと同様に処理する。ただし、部分木の根ノードとその親ノードを結ぶエッジが描画されてしまうのを避けるため、部分木の根ノードの行も取り除く。根の除去の際に、欠損ノードのデータ(行)も除去される。
部分木のバイナリツリーを作成する。
# ツリーの高さを取得 max_h <- floor(log2(N)) # 二分木の部分木を作図 d <- 0.1 ggplot() + geom_path(data = edge_df, mapping = aes(x = coord_x, y = depth, group = edge_id), linewidth = 1) + # エッジ geom_point(data = node_df, mapping = aes(x = coord_x, y = depth), size = 10, shape = "circle filled", fill = "white", stroke = 1, na.rm = TRUE) + # ノード geom_text(data = node_df, mapping = aes(x = coord_x, y = depth, label = value), size = 4, na.rm = TRUE) + # 値ラベル geom_text(data = node_df, mapping = aes(x = coord_x, y = depth, label = index, hjust = label_offset), size = 3, vjust = -2, color = "blue", na.rm = TRUE) + # 位置ラベル scale_x_continuous(labels = NULL, name = "") + scale_y_reverse(breaks = 0:max_h, minor_breaks = FALSE) + coord_cartesian(xlim = c(0, 1), ylim = c(max_h+d, -d)) + labs(title = "binary tree", subtitle = "subtree", y = "depth")

「二分木の作成」のときと同様に処理する。欠損値が含まれるレイヤに na.rm = TRUE を追加すると、警告文が表示されなくなる。元のコードでもグラフ自体には影響しない。
N個のノードを持つ二分木から、指定した部分木のツリーが得られた。
欠損の作成
続いて、二分木の一部のノード(部分木)を取り除いたグラフを作成する。
ノード数と削除する部分木の根を指定して、部分木を作成する。
# ノード数を指定 N <- 63 # (削除する)部分木の根を指定 sub_root_idx <- c(7, 9, 22) # (削除する)部分木のインデックスを作成 del_node_idx <- subtree(sub_root_idx, N) del_node_idx
## [1] 7 9 14 15 18 19 22 28 29 30 31 36 37 38 39 44 45 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63
「部分木の作成」のときと同様にして、削除する部分木のノードのインデックスを作成して del_node_idx とする。
部分木を含まないノードの値を作成する。
ノードの値から部分木に含まれるノードの値を削除する。
# 値を作成 a <- sample(x = 1:N, size = N, replace = TRUE) # 部分木のノードを剪定 a[del_node_idx] <- NA a
## [1] 28 53 34 28 35 7 NA 63 NA 30 45 1 33 NA NA 25 55 NA NA 26 39 NA 12 13 33 ## [26] 12 46 NA NA NA NA 33 3 17 16 NA NA NA NA 10 46 35 34 NA NA 31 36 56 36 43 ## [51] 36 12 24 34 27 NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA
N 個の値 a の内、del_node_idx に含まれる要素を欠損値 NA に置き換える(代入する)。
ノードの描画用のデータフレームを作成する。
# ノードの座標を作成 d <- 0.5 node_df <- tibble::tibble( value = a, node_id = 1:N, index = dplyr::if_else( condition = !is.na(value), true = node_id, false = NA_real_ ), depth = floor(log2(index)), col_idx = index - 2^depth + 1, # 深さごとのノード番号 coord_x = (col_idx * 2 - 1) * 1/(2^depth * 2), label_offset = dplyr::if_else( condition = index%%2 == 0, true = 0.5+d, false = 0.5-d ) # ラベル位置を左右にズラす ) node_df
## # A tibble: 63 × 7 ## value node_id index depth col_idx coord_x label_offset ## <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> ## 1 28 1 1 0 1 0.5 0 ## 2 53 2 2 1 1 0.25 1 ## 3 34 3 3 1 2 0.75 0 ## 4 28 4 4 2 1 0.125 1 ## 5 35 5 5 2 2 0.375 0 ## 6 7 6 6 2 3 0.625 1 ## 7 NA 7 NA NA NA NA NA ## 8 63 8 8 3 1 0.0625 1 ## 9 NA 9 NA NA NA NA NA ## 10 30 10 10 3 3 0.312 1 ## # ℹ 53 more rows
「部分木の作成」のときのコードで処理する。
エッジの描画用のデータフレームを作成する。
# エッジの座標を作成 edge_df <- dplyr::bind_rows( # 子ノードの座標 node_df |> dplyr::filter(depth > 0) |> # 根を除去 dplyr::mutate( edge_id = index, node_type = "childe" # (確認用) ), # 親ノードの座標 node_df |> dplyr::filter(depth > 0) |> # 根を除去 dplyr::mutate( edge_id = index, node_type = "parent", # (確認用) depth = depth - 1, index = index %/% 2, col_idx = index - 2^depth + 1, # 深さごとのノード番号 coord_x = (col_idx * 2 - 1) * 1/(2^depth * 2) ) ) |> dplyr::select(!label_offset) |> dplyr::arrange(edge_id, depth) edge_df
## # A tibble: 74 × 8 ## value node_id index depth col_idx coord_x edge_id node_type ## <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> ## 1 53 2 1 0 1 0.5 2 parent ## 2 53 2 2 1 1 0.25 2 childe ## 3 34 3 1 0 1 0.5 3 parent ## 4 34 3 3 1 2 0.75 3 childe ## 5 28 4 2 1 1 0.25 4 parent ## 6 28 4 4 2 1 0.125 4 childe ## 7 35 5 2 1 1 0.25 5 parent ## 8 35 5 5 2 2 0.375 5 childe ## 9 7 6 3 1 2 0.75 6 parent ## 10 7 6 6 2 3 0.625 6 childe ## # ℹ 64 more rows
「二分木の作成」のときのコードで処理する。
バイナリツリーを作成する。
# ツリーの高さを取得 max_h <- max(node_df[["depth"]], na.rm = TRUE) # 二分木を作図 d <- 0.1 ggplot() + geom_path(data = edge_df, mapping = aes(x = coord_x, y = depth, group = edge_id), linewidth = 1) + # エッジ geom_point(data = node_df, mapping = aes(x = coord_x, y = depth), size = 10, shape = "circle filled", fill = "white", stroke = 1, na.rm = TRUE) + # ノード geom_text(data = node_df, mapping = aes(x = coord_x, y = depth, label = value), size = 4, na.rm = TRUE) + # 値ラベル geom_text(data = node_df, mapping = aes(x = coord_x, y = depth, label = index, hjust = label_offset), size = 3, vjust = -2, color = "blue", na.rm = TRUE) + # 位置ラベル scale_x_continuous(labels = NULL, name = "") + scale_y_reverse(breaks = 0:max_h, minor_breaks = FALSE) + coord_cartesian(xlim = c(0, 1), ylim = c(max_h+d, -d)) + labs(title = "binary tree", subtitle = paste0("height = ", max_h), y = "depth")
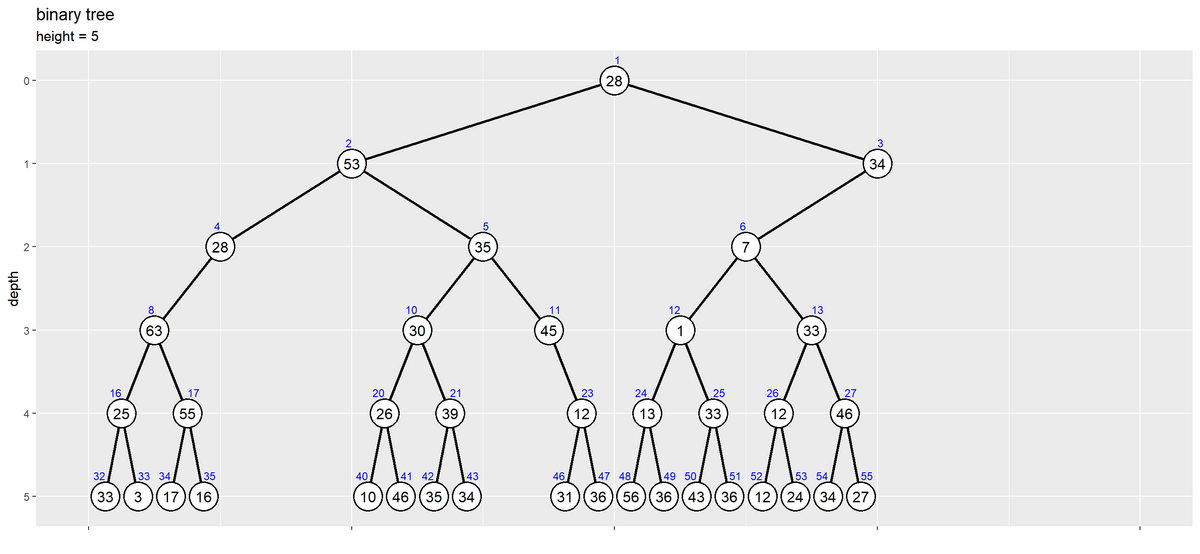
これまでと同様にして処理する。
N個のノードを持つ二分木から、指定した(「部分木の作成」における)部分木のノードが欠損したツリーが得られた。
最後に、値に応じてノードを削除してみる。この例では、根ノードの値未満のノードとその子孫ノードを削除したツリーを作成する。
ノード数を指定して、値を作成する。
# ノード数を指定 N <- 63 # 値を作成 max_v <- 100 a <- sample(x = 1:max_v, size = N, replace = TRUE) a
## [1] 40 72 47 67 20 59 99 89 44 61 20 82 72 51 93 71 61 43 56 4 67 70 13 76 85 ## [26] 25 29 29 90 72 24 89 39 69 30 79 96 50 4 62 60 30 22 96 72 80 15 71 15 22 ## [51] 26 85 57 71 16 74 64 60 25 77 39 46 72
(最大値を指定しているが深い意味はない。)
削除するノードを作成する。
# (削除する)部分木の根を指定 sub_root_idx <- which(x = a < a[1]) sub_root_idx
## [1] 5 11 20 23 26 27 28 31 33 35 39 42 43 47 49 50 51 55 59 61
which() を使って条件を満たすインデックスを作成して、削除する根ノードのインデックスとして用いる。
ノードの値から部分木に含まれるノードの値を削除する。
# (削除する)部分木のインデックスを作成 del_node_idx <- subtree(sub_root_idx, N) # 部分木のノードを剪定 a[del_node_idx] <- NA a
## [1] 40 72 47 67 NA 59 99 89 44 NA NA 82 72 51 93 71 61 43 56 NA NA NA NA 76 85 ## [26] NA NA NA 90 72 NA 89 NA 69 NA 79 96 50 NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA 71 NA NA ## [51] NA NA NA NA NA NA NA 60 NA 77 NA NA NA
先ほどのコードで、バイナリツリーを作成する。

根の値以上のノードのみが残るツリーが得られた(元のツリーの内、根の値以上のノードの全てが残っているわけではない)。
この記事では、インデックスが1からのニ分木のグラフを作成した。次の記事では、インデックスが0からで指定した数に分岐するツリーを作成する。
参考文献
- 大槻兼資(著), 秋葉拓哉(監修)『問題解決力を鍛える! アルゴリズムとデータ構造』講談社サイエンティク, 2021年.
おわりに
ヒープソートのために必要だったので書きました。
それなりに見る図ですし気楽にやるつもりだったのですが、調べてもやり方が見当たらず我流でやることになりました。思いの外面倒でした。だからなかったのか。
読むだけでも面倒だと思いますが、元が面倒なので仕様がないんです。
2023年9月14日は、モーニング娘。の結成26周年です!
ちなみに私は2017年の夏頃からのファンです。これからもよろしくお願いします。
【次の内容】