はじめに
R言語のgganimateパッケージを使ってグラフを動かそうシリーズです。
この記事では、1次元のランダムウォークのアニメーションを作成します。
【他の内容】
【目次】
1次元ランダムウォークの作図
1方向(上下)に移動するランダムウォーク(random walk)のアニメーションを作成します。
gganimate パッケージの関数 transition_reveal() については、「transition_reveal関数【gganimate】 - からっぽのしょこ」を参照してください。
利用するパッケージを読み込みます。
# 利用パッケージ library(gganimate) library(tidyverse)
この記事では、基本的に パッケージ名::関数名() の記法を使うので、パッケージの読み込みは不要です。ただし、作図コードについてはパッケージ名を省略するので、ggplot2 を読み込む必要があります。
また、ネイティブパイプ演算子 |> を使います。magrittr パッケージのパイプ演算子 %>% に置き換えられますが、その場合は magrittr を読み込む必要があります。
1サンプル
まずは、1つのサンプルを描画します。
試行回数を指定して、移動量をランダムに生成します。
# 試行回数を指定 max_iter <- 100 # 乱数を生成 random_vec <- sample(x = c(-1, 1), size = max_iter, replace = TRUE) # ±1 head(random_vec)
[1] -1 1 1 -1 -1 1
試行ごとに -1 または 1 をランダムに(等確率で)割り当てます。1 は正の方向、-1 は負の方向の移動に対応します。
移動量に応じた座標を計算します。
# 試行ごとに集計 trace_df <- tibble::tibble( iter = 0:max_iter, # 試行番号 r = c(0, random_vec), # 移動量 y = cumsum(r) # 総移動量を計算 ) trace_df
# A tibble: 101 × 3
iter r y
<int> <dbl> <dbl>
1 0 0 0
2 1 -1 -1
3 2 1 0
4 3 1 1
5 4 -1 0
6 5 -1 -1
7 6 1 0
8 7 -1 -1
9 8 1 0
10 9 -1 -1
# ℹ 91 more rows
初期値(スタート地点・0回目の結果)を 0 として追加して、各試行までの和(累積和)を cumsum() で計算します。
点の推移のアニメーションを作成します。
# グラフサイズを設定 axis_size <- trace_df[["y"]] |> abs() |> max() # 1次元ランダムウォークのアニメーションを作図 anim <- ggplot() + geom_hline(yintercept = 0, color = "red", linetype = "dashed") + # 初期値 geom_path(data = trace_df, mapping = aes(x = iter, y = y), size = 1) + # 軌跡 geom_point(data = trace_df, mapping = aes(x = iter, y = y), size = 4) + # 現在地点 gganimate::transition_reveal(along = iter) + # フレーム切替 coord_cartesian(ylim = c(-axis_size, axis_size)) + # 描画範囲 labs(title = "Random Walk", subtitle = "iteration: {frame_along}", x = "iteration", y = "y") # gif動画を作成 gganimate::animate( plot = anim, nframes = max_iter+1, fps = 10, width = 8, height = 6, units = "in", res = 250 )
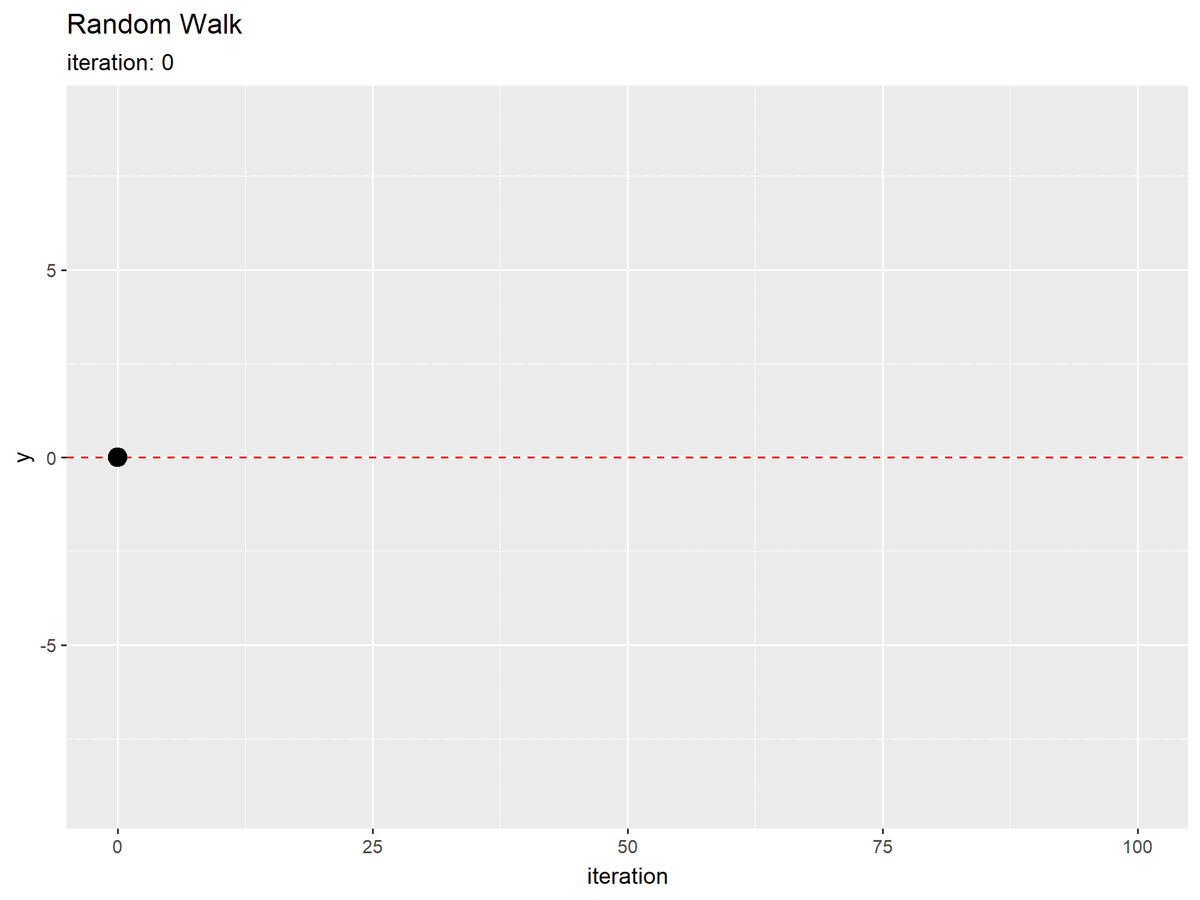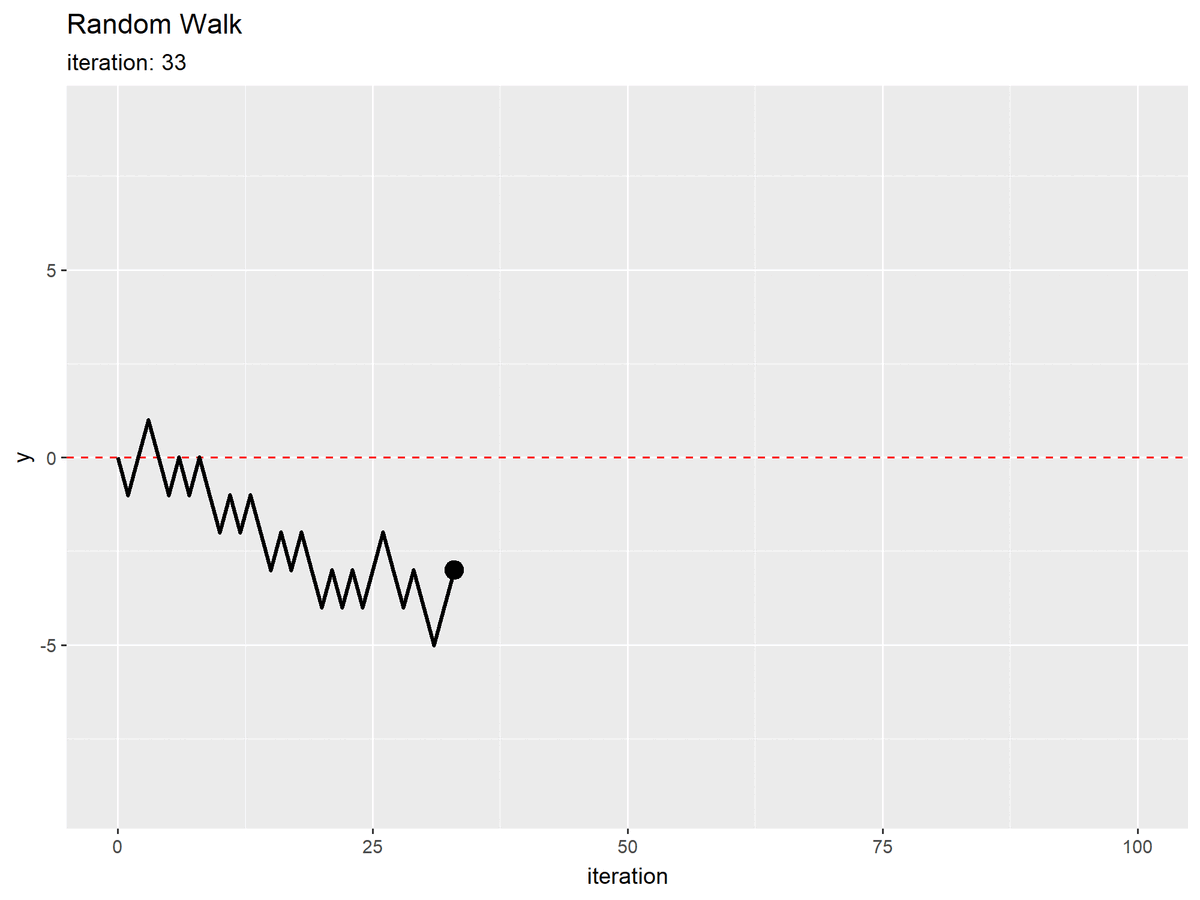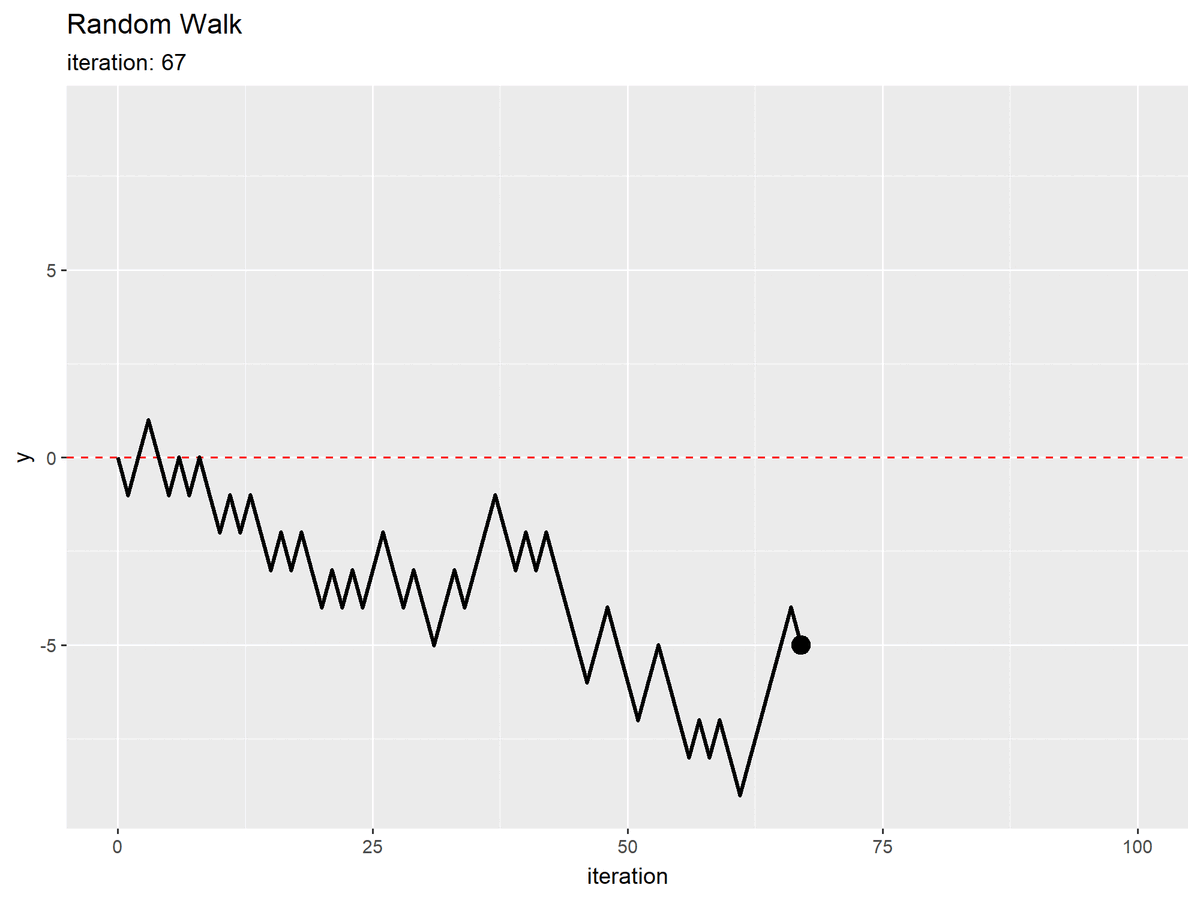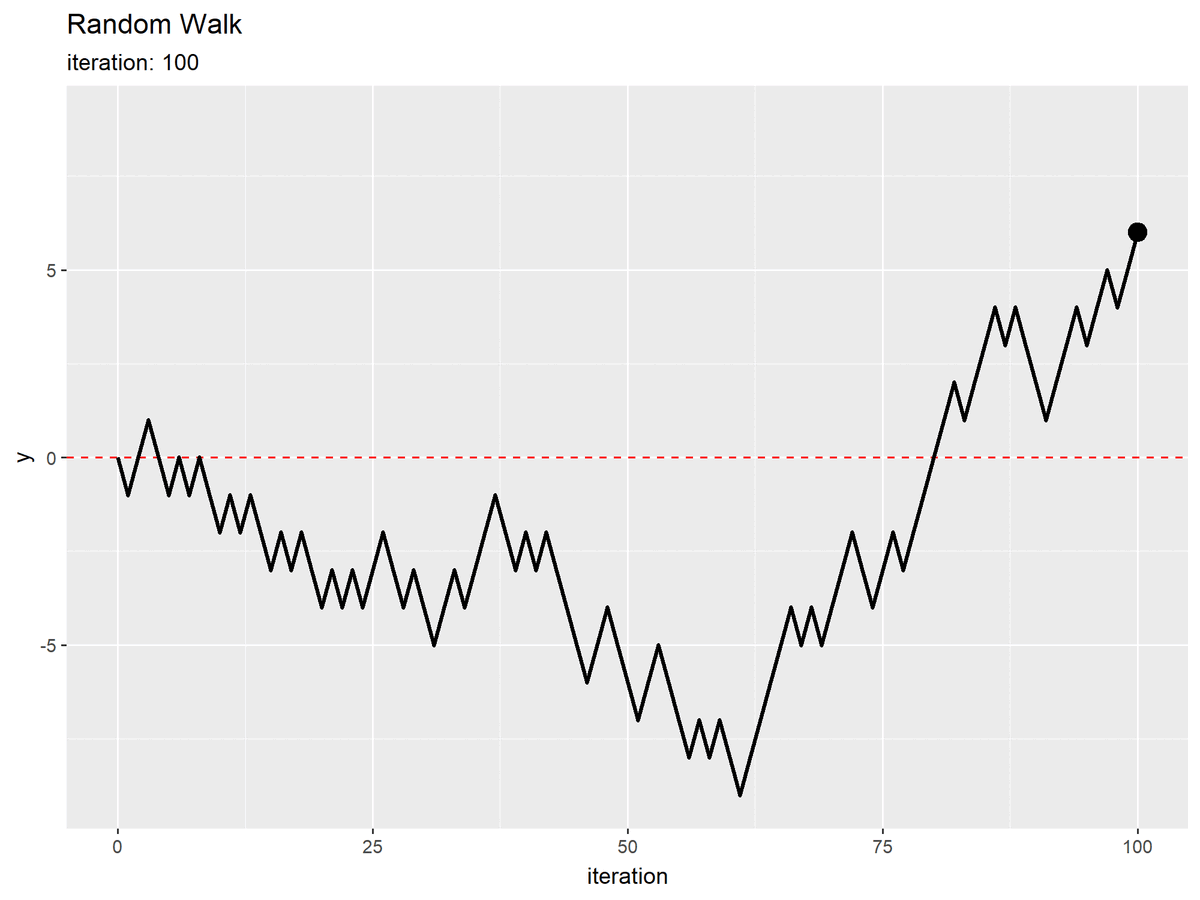
初期値(期待値)を破線で示します。
試行回数(時間)の変化を横軸で表しているので2次元に変化していますが、あくまで縦軸に対してランダムに移動しています。
複数サンプル
続いて、複数のサンプルを並べて描画します。
作図コードについては「GitHub - anemptyarchive/gganimate/.../RandomWalk.R」を参照してください。
・最終結果
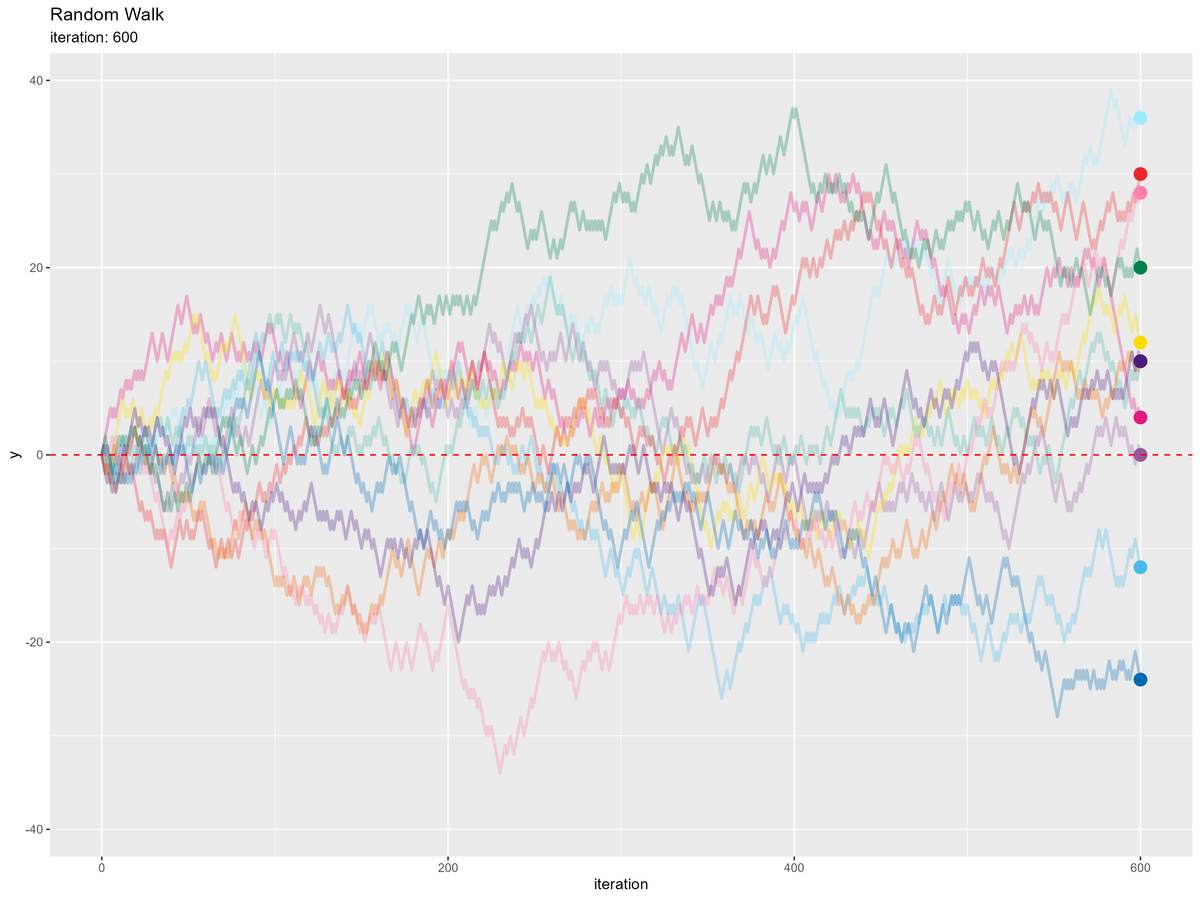
・推移のアニメーション
等確率で移動する場合、初期値が期待値になりますが分散を持ち(散らばり)ます。
この記事では、1次元の(上下に移動する)ランダムウォークを扱いました。次の記事では、2次元の(上下左右に移動する)場合を扱います。
おわりに
transition_reveal()の記事の一部として書き始めたのですが、充実したので別の記事どころか3記事になりました。というわけで続きます。
- 2024.02.14:加筆修正しました。
内容的には変わっていませんが、グラフの装飾周りが良くなりました。
作業負荷(主に改修コスト)を下げるために、複数サンプルのコードを「解説はなしでGitHubを見てね」にしました。今後は他の記事でもこの形式でやっていくつもりです。
【次の内容】